Links
-
New Spherical Nucleic Acid ‘Drug’ Kills Tumor Cells in Humans with Glioblastoma
An experimental spherical nucleic acid drug developed by Northwestern scientists was able to penetrate the blood-brain barrier and trigger the death of glioblastoma cells.
-
Evaluating Esophageal Hypervigilance and Symptom Anxiety
Measuring levels of hypervigilance and anxiety may improve healthcare providers’ understanding of severe esophageal diseases and treatment strategies, according to a Northwestern Medicine study.
-
Hippocampus Creates ‘Shapes of Knowledge’
Neurons in the hippocampus encode a spatial map of learned knowledge, helping humans and other mammals navigate the world, according to a study published in Nature.
-
Antibody Drug Improves Survival for Aggressive Breast Cancer
A new antibody drug demonstrated similar efficacy to currently available therapies to treat advanced ERBB2-positive breast cancer, according to a recent clinical trial.
-
Plotting the Neural Circuitry of Appetite Suppression
Northwestern Medicine scientists have uncovered a neural circuit that drives fear-induced suppression of feeding, according to a study published in Neuron.
-
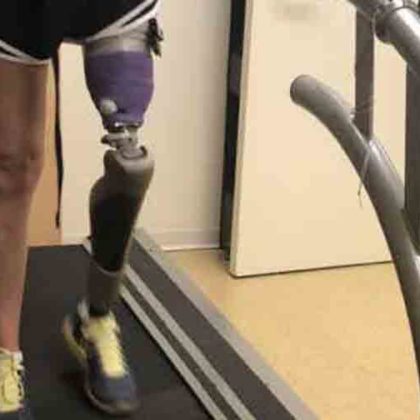
Novel Device Provides Continuous Monitoring of Skin, Prostheses
A multi-disciplinary team of investigators led by Northwestern scientists have developed a novel wireless device that can constantly monitor pressure and temperature between the patient’s skin and prosthesis, improving overall comfort and wellbeing.
-
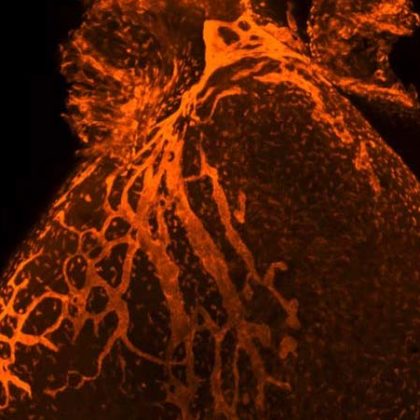
Rethinking Cardiac Repair After Injury
A signaling molecule produced by the lymphatic vasculature could be used to promote cardiac repair after heart attack, according to a Northwestern Medicine study published in Nature.
-
New Therapy Targets Breast Cancer Metastases in Brain
A new combination therapy targeting breast cancer tumors in the brain dramatically decreased tumor size and increased survival in mice, according to a new study.
-
Gene Therapy Could Treat Atrial Fibrillation
Targeting oxidative stress with a genetic therapy reduced atrial fibrillation in animal models of disease, making this a promising future treatment, according to a study published in Circulation.
-
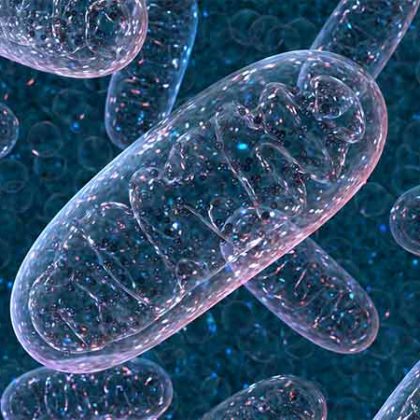
Mitochondrial Metabolism Shows Promise as Target for Cancer Therapy
Northwestern Medicine investigators have discovered that the growth of cancerous tumors requires the activation of a specific biochemical process within the mitochondria of tumor cells, showing potential as a new target for cancer therapy.